In this study, the growth inhibitory effect of garlic on H. pylori
observed. In addition,
synergistic effect was found in combination garlic and omeprazole. However, no synergistic or antagonistic
effect is observed between garlic and amoxycillin, clarithromycin or metronidazole
. Several laboratory studies have shown in the antibacterial effect of Allium vegetables. Antibacterial activity varies depending on the type of product
method and degree of maturity. All experiments in this study were conducted with one party
garlic extract and commercial garlic tablets. Antibacterial effect of garlic was reported earlier on
Gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including antibiotic-resistant strains. Recently, two studies also described an antibacterial effect of garlic >>
<< pylorus against H.. ,
Garlic, like all Allium vegetables contain a wide range thiosulphinates like allitsyn are
is responsible for antibacterial activity. Selective removal or prevention thiosulphinates
their education inhibition alliinase strattera without prescritpion eliminates the antibacterial activity of garlic. When commercial garlic tablets tested in this study were
compared based on their content allytsyna, no differences in antibacterial activity were found. In addition, strong antibacterial effects were observed in raw garlic extract, which was
revealed a high concentration allytsyna, supporting an important role in allitsyn >> << antibacterial activity of garlic. Theoretically, as thiosulphinates and omeprazole (substituted benzimidazole) may have similar
mechanism of antibacterial activity. As indicated in omeprazole, allitsyn can also contact
SH-groups, for example, bacterial enzymes
and nutrients, such as cysteine. ,
Competition between garlic and omeprazole to link the existing SH-groups may contribute to synergy effects in
against the concentration of both substances. The presence of important enzymes in the cell membrane
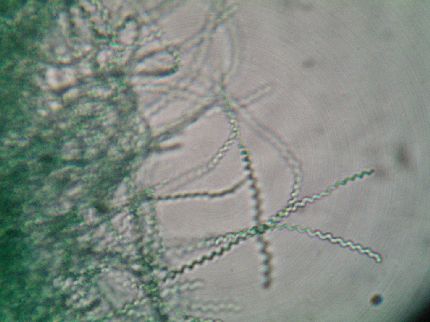
H. pylori (eg, urease) may contribute to a strong antibacterial effect from
garlic and omeprazole against this organism. MIC values for the crude extract of garlic and commercial garlic tablets were quite low, so that
in vivo effect of garlic in the stomach possible. In vivo studies have shown
therapeutic potential of garlic in humans. Gastric environment, such as pH, temperature and
dietary factors also influence the antibacterial activity of omeprazole and garlic in comparison with in vitro
conditions. Intragastric acidity is unlikely to be a problem as omeprazole needs acid
catalysation its antibacterial activity and antibacterial activity of garlic is found in
presence of buffer pH 2. Antibacterial effect of garlic and synergistic effect of garlic in combination with omeprazole
<< >> could be an interesting alternative therapy of infection H. pylori. << >> Further studies on the combined effect of << >> omeprazole and garlic are justified. . << >>
No comments:
Post a Comment